Amnesia is not a new term. We often meet people afflicted with memory loss but as a layman we find it difficult to recognize. Amnesia or memory loss can be cataloged as a condition where the mental attentiveness or memory of a person is distressed or misplaced. This loss of memory may be provisional or enduring depending upon the reasons from which it has advanced. These causes may be classified under diverse categories. The psychosomatic aspects correlated with amnesia are mental disorder, post-traumatic stress and it may also emerge as an impulsive event of transient global amnesia.
Meaning of Amnesia?
Amnesia has been a subject of fashionable focus for the big screen as well as television. In an uncomplicated sense amnesia is loss of ability to recollect the stored information from the memory store of brain at a precise interlude of time. This state can be accomplished by any corporeal grievance to the brain as well as intake of any noxious matter which may blight the accurate implementation of brain. Any harrowing as well as poignant event may be the root cause of amnesia.
How amnesia originates?
Any malady or damage which impinges the apt execution of brain can weaken the memory. The function of memory is paired with diverse fractions of brain which take action concurrently at a time. Any damage to brain predominantly to the limbic system, hippocampus and thalamus can be the root cause of the turmoil what we call as amnesia. Limbic system is united with the formation of memories as well as it directs our sentiments. Scientists at the University of Liverpool have found that memory loss can crop up if any dent to hippocampus is caused. Amnesia may be neurological as caused by stroke. Encephalitis caused by herpes simplex virus or an autoimmune reaction to cancer may also be accountable for memory loss. Celiac disease may be connected with amnesia but there is not a sturdy corroboration to sustain this inspection.
Oxygen deficiency or loss of suitable supply of oxygen to brain, carbon monoxide poisoning, respiratory distress as well as heart attack is also somehow associated with loss of memory. Unwarranted intake of a sleeping drug, ambient also causes amnesia. Bleeding of the area between the skull and brain also known as subarachnoid hemorrhage as well as brain tumor also causes memory loss. Electroconvulsive therapy also known as electric shock therapy given to an individual suffering from depression may also be sometimes associated with amnesia. Electroconvulsive therapy is also sometimes used for treating schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and catatonia but the memory loss is always impermanent. Head injuries caused during accidents also lead to momentary memory loss but they are not extended lifelong. Functional or dissociative amnesia may be caused by emotional shock for instance a person who has suffered from any sadistic origin, sexual mistreatment or child exploitation. A person engrossed in any fanatic operation, battle or an innate catastrophe may also experience amnesia. Any situation which may escort to psychological stress can also be tied with amnesia.
Categories of amnesia
Amnesia can be cataloged under diverse ranks depending upon the precise foundation.
1. Anterograde amnesia
It is a condition of body when a human being finds it tricky to bear in mind the enduring episodes after a rigorous head grievance. The person retains all the information regarding his identity and preserves all the childhood activities but disregards daily activities. Individuals uncover that they are utterly forgetting things and incidents that are taking place because the information is not being reassigned from the short-term memory store to the long-term memory store. A Bollywood blockbuster hit entitled Ghajini released in 2009 was based on anterograde amnesia. Aamir khan played the character of Sanjay Singhania who encountered brutal head damage after being trodden by the villain Ghajini and became a patient of this anarchy.
2. Retrograde amnesia
It is just contradictory to anterograde amnesia. In this condition the person remembers the daily ongoing events but forgets the earlier period of his life. The individual is proficient in shaping fresh memories but is incapable of recollecting the information before the calamity.
3. Wernike-Korsakoff's psychosis
This condition is caused by disproportionate utilization of alcohol. The short-term memory of the victim may linger customary but he may experience intricacies allied to summon up uncomplicated truths, faces of different people and other behavioral prototypes. If this condition reigns the person may suffer from remarkable neurological problems like uncoordinated movements and loss of sensation in fingers and toes. If this starts happening it will be too overdue for the patient to discontinue drinking. It may also be caused by undernourishment and is coupled with thiamine paucity.
4. Traumatic amnesia
This category amnesia may be caused by a stern non-penetrative puff to the head in a road mishap. The brain is wounded eventually ensuing loss of consciousness for few seconds to harsh coma.
5. Infantile/childhood amnesia
In this case the person is incapable of recalling the events of his childhood as the name designates. Many researchers have put forth their theories to substantiate this kind of amnesia. Freud says that it is a class of sexual despotism while others believe that it may be correlated with language development. Some shore up that few areas of brain united to memory are not effusively full-grown.
6. Hysterical amnesia
It is also tenured as fugue amnesia. It incorporates all those episodes of amnesia allied with psychological trauma. This type of amnesia is as a rule transitory and is elicited with the inception of traumatic event which mind finds thorny to mend. The person is unable to forget the harrowing event but his typical memory revisits back after few days.
7. Post-hypnotic amnesia
The events combined with hypnosis cannot be recollected from memory.
8. Source amnesia
The individual remembers the information but fails to spot out from where he has got these facts.
9. Blackout phenomenon
In this case the person is unable to recall petite hunks of information and this type of amnesia is caused by intense drinking.
10. Prosopamnesia
In this case the individual is unable to identify the faces of people. People attain this type of amnesia in their life span or may be born with it.
11. Transient global amnesia
This is a momentary loss of all types of memory. The person suffering from transient global amnesia is unable to outline new memories or in effortless terms he or she has very extreme type of anterograde amnesia. The loss of past memories is milder. This form of amnesia is atypical in natural history. The victim is generally grown-up in age and also suffers from vascular convolutions.
Features of amnesia
People suffering from amnesia appear confused as they find themselves difficult to handle new objects as well as recalling preceding information. Such people uncover themselves perturbed to work in offices, schools and other job places. Sometimes bogus memories may be outlined. A very appealing study entitled Do you know what you did on 13 March, 1985 points toward the story of a person who constantly furnishes dissimilar retorts whenever the identical question is being solicited. Neurological predicaments like uncoordinated body movements and sometimes tremors are also perceived. Mystification and bafflement is very frequent. Setbacks with short-term memory, unfinished or inclusive loss of memory are also illustrious. Knack to be acquainted with people as well as places is also ebbed. Amnesia is different from dementia which rivets other cognitive hitches where the individual finds it thorny to clutch out daily activities.
Diagnosis of amnesia
Amnesia can distress both male and female and can transpire at any era. The health professional first of all make an effort to find out all the feasible explanations that may be correlated with the memory loss like dementia, Alzheimer's disease, depression, or a brain tumor. The doctor entails the comprehensive medical history of the individual from the family associates of the patient. After that the doctor finds out whether the person is finding complexity in recalling innovative or precedent events. Then he tries to find out how and when the troubles combined with memory have initiated. After that he gets the aspects of family whether there is any neurological disorder present in the family account or whether the person is buffed to alcohol or some illegitimate drugs like cocaine or has been a patient of depression. Finally he also finds out whether the patient had suffered from cancer or any sort of seizures.
The physician also carts out some physical exams of the patient to ensure patients' reflexes, sensory function, balance and some other facets of brain and nervous system. The doctor also verifies the judgment aptitude, short and long-term memory of the individual. The memory appraisal facilitates the doctor to find out the degree of memory loss and then he can decide the unsurpassed cure for the patient. In order to find out the physical damage or any idiosyncrasy in the brain the doctor may also recommend the patient to undergo MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan. In MRI the machine uses magnetic as well as radio waves to dig up specified images of any fraction of the body. This contrivance is much superior to the CT scanning tool as it detects the brain tumor very fittingly. The appliance uses X-rays. A CT scan senses bleeding in any division of the brain at superior exactness. The doctor may also direct the patient to undergo Electroencephalogram which takes metaphors of brain while the individual is performing any cognitive chore like a work united with accepted wisdom. This assists the doctor to sense the spot and enormity of brain bustle engaged in numerous brands of cognitive gatherings. Reflections are crafted by using electrodes to scrutinize the quantity of electrical activity at diverse peaks on the patient's scalp. Blood tests can also be carried out as they distinguish any contagion or nutritional deficiency leading to memory loss in attendance or not.
Treatments available for amnesia
In majority of the cases of amnesia the syndrome recovers without being treated at all. In circumstances where a brain injury is involved, the disease calls for treatment if accessible. Psychotherapy has been found to give hopeful results and even hypnosis can be used in recalling events. Family shore up and collaboration plays an effectual role in healing of the patient. If the patient is encircled with pictures, materials and music he heals quicker. The foremost aim of treatment executes with the cure of memory loss. An occupational therapist can use all the precedent information and may facilitate the patient to shape new memories. Learning techniques for categorizing information can also make it easier to amass information. Learning how to make paramount use of personal digital assistant (PDA), such as an iPhone or Blackberry can also help the patient to carry out daily activities without complexity. There are currently no drugs accessible for the treatment of patients suffering from amnesia. However, in case of Wernicke-Korsakoff's psychosis proficient uptake of thiamine can help in recuperating from amnesia. Whole grain cereals, legumes, nuts, lean pork, and yeast are prosperous resources of thiamine.
Complications associated with patients of amnesia
The extent of amnesia fluctuates with the dilemmas linked with memory. By discontinuing the use of lethal substance the person can recollect his memory within few hours. However, if the brain has received a harsh injury then it may take weeks, months, or years to recover. In some cases amnesia can never be improved. The diagnosis basically depends upon the level of the brain trauma. If memory loss has cropped up because of the uptake of any noxious stuff then by impeding the uptake of that core the person may recover but if the brain is indignant the person may take time to heal. Such persons necessitate accurate family support and a proper care by the doctor.
Amnesia and Memory
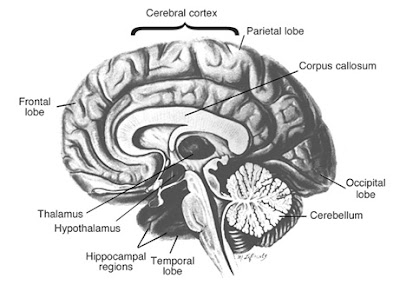
Human brain strictly speaking is a very astounding organ. It bestows humans the skill to sense, sketch, articulate and envisage. It also offers the command to formulate and pile up memories. In a physiological sense memory is essentially the chemical or even structural alteration stirring in synaptic transmissions between neurons. This progression shapes a sort of pathway tenured as memory trace. Signals can take a trip along these memory traces through brain. Configuration of memory is a multifarious process and it rivets dissimilar fractions of brain, counting the frontal, temporal and parietal lobes. Dent or disease in any of these divisions of brain can upshot in anecdotal grades of memory loss. There are unlike forms of memory for instance, procedural memory distressed with automated skills and declarative memory bonded with personal abstracts. In broad-spectrum only one type of memory is prejudiced. For instance, a person may disregard the features of a person's distinctiveness but does not forget the learned talents like playing guitar.
The sector of brain concerned with memory construction is phrased as limbic system and it embraces hippocampus, amygdala, and firm cortical segments. Apart from recollection of memory, the limbic system also partakes in coordination of emotion and motivation. Some role of endocrine system is also carried out by the limbic system. For a short-term memory to get translated into a long-term memory the process of consolidation must take place. During consolidation short-term memory is repetitively triggered and definite chemical and physical changes transpire in brain that is accountable for long-term memory configuration. If during the process of reiterated inauguration of the short-term memory a physical injury or trauma crops up then consolidation stops and the process of long-term memory formation fails. We can say that memories cannot be stocked up for extended term admittance and this is the stipulation that arises in anterograde amnesia. It is usually judged that consolidation takes place in the hippocampus situated in the temporal province of brain. Medical studies designate that the frontal and temporal, lobes are normally smashed up during the head grievance. This sustains the data that why the proportion of people afflicted from anterograde amnesia is elevated. If the hippocampus are damaged the person is able to recall older memories but cannot form the new ones.
The Amnesic Syndrome
Medical studies depict the anecdote of a famous amnesic patient Henry Molaison or H.M. who underwent a surgery for the treatment of stern epileptic seizures in 1953. During this surgery the hippocampus of H.M. was dissected bilaterally which failed to cure the symptoms of epilepsy but resulted in amnesia. Animal researchers discerned that along with hippocampus the cortical regions predominantly entorhinal, perirhinal, and parahippocampal cortices were also scratched during the surgery and that's why H.M. became amnesic. After this unpleasant incident Stuart Zola-Morgan and Larry Squire accomplished various studies on monkeys to divulge the legitimacy. Dissecting different regions of brain lastly portrayed the precision. It is currently apparent that any dent to the amygdala is not correlated with memory loss but any rigorous harm to the cortical regions and the hippocampus can elicit memory loss. The most attention-grabbing verity is that amnesia can crop up if a hard blow to the cortical regions adjoining hippo-campus is given without damaging the hippocampus.